| |
|
| 美国MOBIO 强力土壤DNA大量提取试剂盒(PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit) |
|
|
PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit
OverviewFor efficiently isolating microbial DNA of high quality and purify from large quantities of soil - great for samples with low microbial load
Order
| Description |
Catalog # |
Price |
| 10 preps |
12988-10 |
N/A |
|
Features
- Purifies DNA from 10 g soil in 30 minutes - means NO time spent on multiple small sample processing
- Increases detection sensitivity on samples with a low microbial load
- Provides high quality DNA that is free of PCR inhibitors including humic substances
- Purified samples are suitable for PCR and QPCR
Description
The PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit is our next-generation kit designed for processing large quantities of any soil or environmental sample with high or low microbial load. Based on reagents from the PowerSoil® DNA Isolation Kit, the PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit uses our novel, patented Inhibitor Removal Technology® to remove PCR inhibiting compounds, including humic substances, and the brown color often associated with soil DNA. The kit is ideal for environmental samples that contain high humic substance content, including compost, sediment and manure. PCR analysis has been used to amplify DNA purified from microorganisms including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus anthracis), fungi (e.g. yeasts, molds), algae, and actinomycetes (e.g. Streptomyces).
The PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit increases your ability to study microbial diversity in even the most difficult sample types, such as those which contain high humic levels or low microbial load. Our 50 ml Vortex Adapter for cell lysis and a centrifuge capable of spinning 50 ml tubes are required for maximum performance.
Sample Kit
Click to try a sample.
Research and Development
| High Yield, Intact Genomic DNA |
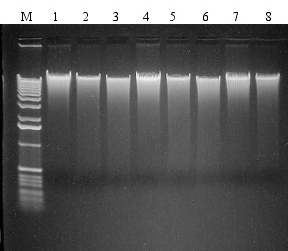
Total genomic DNA was isolated from 8 different soil samples using the PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit. 0.75 µg of each isolated DNA was analyzed on 1 % TAE agarose gel and ethidium stained. M = Marker DNA. Soil types are identified in the table below.
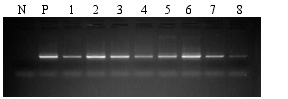
One microliter of total genomic DNA isolated using the PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit was PCR amplified using primers to the Bacillus spp. Amplified DNA was analyzed on 0.8% TAE agarose and ethidium stained. The amount of PCR fragment produced in each sample is representative of the relative amount of the template sequence in the purified DNA. Different soil sources will have different types and amount of organisms providing genomic DNA. N = Negative control lacking template. P = Positive control template. Soil types and amount are identified in the table below.

One microliter of total genomic DNA isolated using the PowerMax® Soil DNA Isolation Kit was PCR amplified using primers to the Streptococcus spp. DNA was analyzed on 1 % TAE agarose and ethidium stained. The amount of PCR fragment produced in each sample is representative of the relative amount of template sequence in the purified. Different soil sources will have different types and amount of organisms providing genomic DNA. N = Negative control lacking template. P = Positive control template. Soil types and amount are identified below.
| Sample Lane |
Type |
Amount processed (grams) |
| 1 |
Iowa corn field |
10 |
| 2 |
So. California strawberry field |
10 |
| 3 |
Cardiff estuary sediment |
10 |
| 4 |
Carlsbad lagoon sediment |
10 |
| 5 |
Home compost |
5 |
| 6 |
San Diego City compost |
5 |
| 7 |
Commercial potting mixture |
2.5 |
| 8 |
Commercial peat moss |
2.5 | |
 Click over image to enlarge
Specifications
| Format |
Silica Spin Filter Tubes |
| Method |
Bead Beating |
| Sample Size |
Up to 10 grams |
| Binding Capacity |
Up to 1 mg per filter |
| Throughput |
1 - 24 samples |
| Time |
30 minutes |
| Equipment Required |
Vortex and Centrifuge |
| Soil Samples Tested |
|
| Aquifer Sediment |
Manure |
| Clay |
Marine Sediment |
| Fecal Intestinal Tract |
Oil-saturated Soil |
| Forest |
Potting Soil |
| Fungal Mat |
Sand |
| Loam |
Sewer Sludge |
Storage ConditionsStore at room temperature for up to 2 years.
Publications
- Berthrong, S.T., Schadt, C.W., Pineiro, G., and Jackson, R.B. Afforestation Alters the Composition of Functional Genes in Soil and Biogeochemical Processes in South American Grasslands. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 76(19): 6240-6248 (2009).
- Ferrando, L. and Tarlera, S. Activity and Diversity of Methanotrophs in the Soil-water Interface and Rhizospheric Soil from a Flooded Temperate Rice Field. Journal of Applied Microbiology . 106(1): 1364-5072 (2008).
- Kennedy, P.G., Bergemann, S.E., Hortal, S., Bruns, T.D. Determining The Outcome Of Field-based Competition Between Two Rhizopogon Species Using Real-time PCR. Molecular Ecology. 16(4): 881-890 (2007).
|
|